按照CSMN的层级写一个spring boot项目
约 727 字大约 2 分钟
2025-07-11
这篇博客更强调思路(写代码的顺序),更详细的步骤可以看: IDEA+VUE 创建 springboot 项目和对应的前端项目
数据库内容
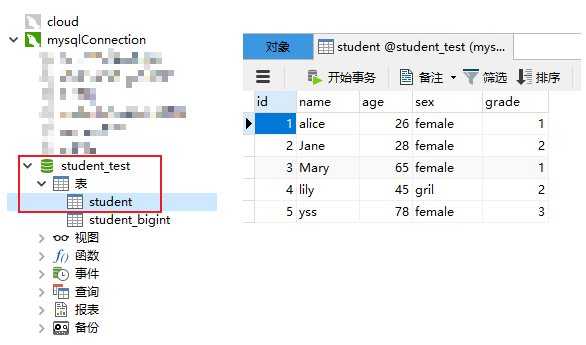
Spring boot 项目结构
创建项目步骤看前言中的博客链接。
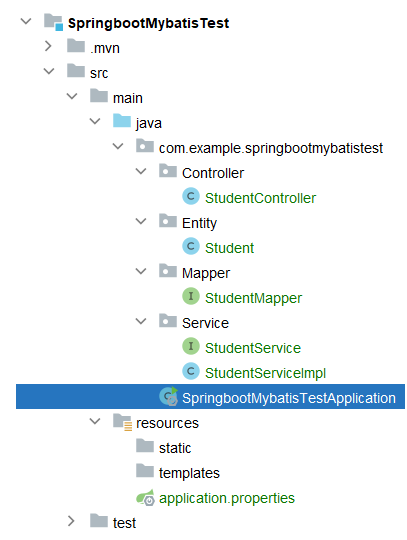
配置数据库信息
# 端口号默认8080,可以修改
#server.port=8081
# 驱动类名称
spring.datasource.driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student_test?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.username: root
spring.datasource.password: 1234
# 配置mybatis的日志,输出到控制台
# mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
# 开启mybatis的驼峰命名自动映射开关 a_column --> aCloumn 建议开启
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true添加注解扫描类
先在 SpringbootMybatisTestApplication.java 上加注解扫描 mapper 类
package com.example.springbootmybatistest;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.example.springbootmybatistest.Mapper") // 🚩 注意这里要有注解
public class SpringbootMybatisTestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootMybatisTestApplication.class, args);
}
}Spring boot 项目从上到下分层,但写代码的时候从下往上写
mapper 和 dao 意思一样,但是在 springboot 项目中,与数据库交互的层叫 mapper 。
spring boot 四层结构可以记忆为 CSMN(吃什么呢)。
如果是 dao 层,可以记忆为 CSDN
【CSMN:吃什么呢】
- Controller:控制层,和前端交互
- Service:业务逻辑层,处理具体业务逻辑
- Mapper:与数据库交互
- Entity:存放实体类,类的属性和数据库中表的属性对应(如有下划线,改为小驼峰)
Entity
存放实体类,类的属性和数据库中表的属性对应(如有下划线,改为小驼峰)
package com.example.springbootmybatistest.Entity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
private int grade;
}Mapper
与数据库交互。
package com.example.springbootmybatistest.Mapper;
import com.example.springbootmybatistest.Entity.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentMapper { //🚩 注意mapper是interface
@Select("select * from student")
List<Student> findAll();
}Service
业务逻辑层,处理具体业务逻辑。
如果代码复杂,可以把 Service 分成接口 Service 和实现 ServiceImpl
如果代码不复杂,可以直接写一个 StudentService
这里以 StudentService + StudentServiceImpl 为例
package com.example.springbootmybatistest.Service;
import com.example.springbootmybatistest.Entity.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentService {
List<Student> findService();
}注意两个注解 @Service 和 @Autowired
package com.example.springbootmybatistest.Service;
import com.example.springbootmybatistest.Entity.Student;
import com.example.springbootmybatistest.Mapper.StudentMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service // 🚩 注意这里要有注解
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService { // 🚩 继承StudentService
@Autowired // 🚩 注意这里也要有注解
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
public List<Student> findService() {
return studentMapper.findAll();
}
}Controller
控制层,和前端交互。
先在 MydemoApplication.java 上加注解扫描 mapper 类 @MapperScan("com.example.mydemo.mapper")
package com.example.springbootmybatistest.Controller;
import com.example.springbootmybatistest.Entity.Student;
import com.example.springbootmybatistest.Service.StudentServiceImpl;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController // 🚩 注意这里要有注解
@RequiredArgsConstructor // 🚩 注意这里要有注解
public class StudentController {
private final StudentServiceImpl service;
@GetMapping("/findAll")
public List<Student> ss(){
List<Student> service1 = service.findService();
return service1;
}
}运行项目
打开 SpringbootMybatisTestApplication.java 右键 Run
打开浏览器,输入 http://localhost:8080/findAll 出现下图,运行成功。

